Soil Remediation Case Studies: Metal Stabilization Product Blastox® 215
Product Chemistry
Blastox® 215 is a complex calcium silicate chemistry listed as US EPA Best Demonstrated Available Technologies (BDAT) for stabilizing heavy metal wastes, especially lead and cadmium. Custom chemistries are also available to stabilize chromium and other toxic metals. These soil remediation case studies will explain how Blastox works.
The Blastox® stabilization process has three proven stabilization steps:
- Creation of an alkaline waste matrix in which various heavy metals become more resistant to acidic leaching;
- Addition and substitution reactions change the chemical form of the lead from a lead oxide, carbonate or
hydroxide to a lead silicate, which is significantly less soluble than most other lead compounds; - Hydration reactions physically encapsulate the waste, limiting water access and leaching.
The following is a partial list of summaries for projects recently using Blastox®
Location: Firing Range Andover, MD Date: 2011 Client: Government contractor
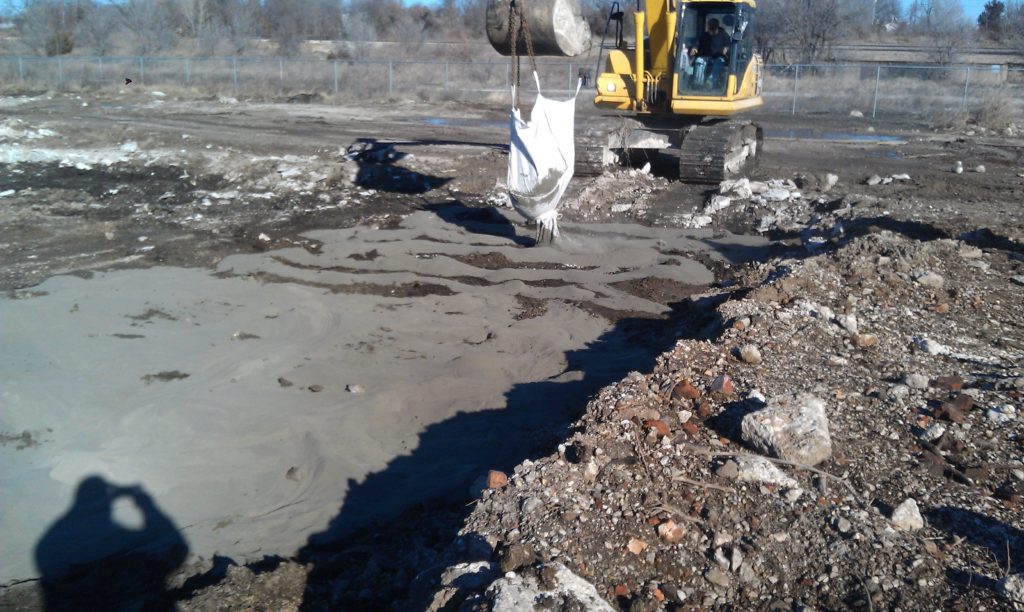
This project had unusually high lead TCLP, some > 1000 mg/l. The remediation contractor, which performed its own treatability tests, reported that the hot spots were successfully treated with a 5% dose and the rest of the areas averaged 2%. Approximately 1100 tons of soil were successfully managed as a non-hazardous waste.
Location: Former Auto Assembly Plant St. Louis, MO Date: 2010-2011 Client: Demolition and remediation contractor
The general contractor that dismantled the plant and removed subsurface structures, was also contracted to remediate contaminated soil. Prior to modern waste disposal regulations, the assembly plant dug trenches on the plant property and used them to burn debris and bury waste. Lead solder, e-coat, and related lead bearing manufacturing debris was buried in several areas and caused soil contamination in excess of 100 mg/l TCLP. The contractor had tried a different lead stabilization reagent for a small initial soil removal, but it required an 8% dose rate. J Carpenter Environmental and TDJ did treatability work with Blastox® and found that the dose rate could be cut in half to 4%. More than 10,000 tons of soil were stabilized with Blastox® and removed from the site.
Location: Abandoned Industrial Property near School in Chicago, IL Date: 2011 Client: Government contractor
An abandoned industrial property in the Greater Chicago area needed to be cleaned up before it could be put back into productive use. When tested via the TCLP without any reagent, the leach values for the hazardous soils ranged from 6.3 mg/l to 189 mg/l. Based on their successful use of Blastox® 215 at another site, the contractor contacted J Carpenter Environmental to see what dose rate would be required. In conjunction with J Carpenter Environmental, TDJ Group conducted a treatability study and concluded that XX dose of reagent would be sufficient. Tons of soil were
successfully stabilized on-site using Blastox® 215.
Regulatory Compliance with Leach Test Protocols
Blastox® was developed to provide long-term stabilization of heavy metals, and accordingly it allows compliance with the USEPA Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP). Additionally, it can be used to comply with EPA’s, the Multiple Extraction Procedure (MEP, Method 1320) and with the Synthetic Precipitation Leach Procedure (SPLP, EPA Method 1312). Blastox chemistry has been tested by the US EPA, US Department of Defense (DoD), Army Corps of Engineers Research Laboratory, US Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), State Departments of Transportation (DOTs).